多线程 - IOS - NSOperation & NSOperationQueue
前言
一、NSOperation
二、NSOperationQueue
三、队列的添加流程
四、DispatchWorkItem
五、队列的执行流程
六、NSOperation添加依赖
七、NSOperation添加额外操作
通过对GCD的初步总结之后,先放松一下大脑,暂停一下GCD更深层的探索。先总结一下基于GCD更高一层封装的NSOperation & NSOperationQueue。 (由于OC(GNU)和swift的源码实现基本是一致的,其中最大区别是swift没有使用KVO,而是手动监听操作的状态变化。所以今天主要以最新的swift的foundation源码分析其底层原理)
相对GCD的核心优势:
1、操作之间可以添加依赖关系。
2、可以使用KVO观察对操作执行状态的更改:isExecuteing、isFinished、isCancelled。
一、NSOperation
NSOperation是执行操作的对象,类似GCD中的block。日常开发中,一般是使用其子类NSInvocationOperation、NSBlockOperation,或者自定义NSOperation的子类。
在swift中,NSInvocationOperation已经被废弃掉了,一般只使用NSBlockOperation,当业务逻辑比较复杂的情况下,可以自定义NSOperation的子类。
1、NSOperation的属性
//双向链表结构
internal var __previousOperation: Unmanaged<Operation>?
internal var __nextOperation: Unmanaged<Operation>?
//下一个优先级操作
internal var __nextPriorityOperation: Unmanaged<Operation>?
//当前的队列
internal var __queue: Unmanaged<OperationQueue>?
//依赖的操作集合
internal var __dependencies = [Operation]()
//被依赖的操作集合
internal var __downDependencies = Set<PointerHashedUnmanagedBox<Operation>>()
//为完成的依赖数量
internal var __unfinishedDependencyCount: Int = 0
//操作完成时设置的回调
internal var __completion: (() -> Void)?
//名称标识
internal var __name: String?
//保存的DispatchWorkItem
internal var __schedule: DispatchWorkItem?
//状态
internal var __state: __NSOperationState = .initialized
//优先级
internal var __priorityValue: Operation.QueuePriority.RawValue?
//缓存的就绪状态
internal var __cachedIsReady: Bool = true
//是否取消
internal var __isCancelled: Bool = false
//服务质量(代替优先级)
internal var __propertyQoS: QualityOfService?
//条件锁
var __waitCondition = NSCondition()
//锁
var __lock = NSLock()
//原子锁
var __atomicLoad = NSLock()
从NSOperation的属性来看,它是在队列中是双向链表结构。
其中NSOperation的内部状态如下:
enum __NSOperationState : UInt8 {
case initialized = 0x00 //初始化
case enqueuing = 0x48 //正在排队
case enqueued = 0x50 //排队结束
case dispatching = 0x88 //正在分发
case starting = 0xD8 //正在开始
case executing = 0xE0 //正在执行
case finishing = 0xF0 //完成中
case finished = 0xF4 //完成
}
2、 当NSOperation在没有添加到队列中,就执行start方法时,它不会开启线程,而是会在当前线程执行。
func testStart() {
let op = BlockOperation {
print("1\(Thread.current)")
}
op.start()
}
打印结果:
1<_NSMainThread: 0x6000010847c0>{number = 1, name = main}
3、NSOperation的start和main有什么区别
open func start() {
//当前状态
let state = _state
//操作的状态为完成,直接return
if __NSOperationState.finished == state { return }
//状态校验
if !_compareAndSwapState(__NSOperationState.initialized, __NSOperationState.starting) && !(__NSOperationState.starting == state && __queue != nil) {
switch state {
case .executing: fallthrough
case .finishing:
fatalError("\(self): receiver is already executing")
default:
fatalError("\(self): something is trying to start the receiver simultaneously from more than one thread")
}
}
if state.rawValue < __NSOperationState.enqueued.rawValue && !isReady {
_state = state
fatalError("\(self): receiver is not yet ready to execute")
}
let isCanc = _isCancelled
//如果没有取消,则执行操作
if !isCanc {
//状态更改为正在执行状态
_state = .executing
Operation.observeValue(forKeyPath: _NSOperationIsExecuting, ofObject: self)
//由队列执行,主要调用了main
_queue?._execute(self) ?? main()
}
//操作结束后更新完成状态
if __NSOperationState.executing == _state {
_state = .finishing
Operation.observeValue(forKeyPath: _NSOperationIsExecuting, ofObject: self)
Operation.observeValue(forKeyPath: _NSOperationIsFinished, ofObject: self)
} else {
_state = .finishing
Operation.observeValue(forKeyPath: _NSOperationIsFinished, ofObject: self)
}
}
//main方法
open func main() { }
由源码可以知:当操作执行时,会调用start方法,在start方法中进行状态判断,当非取消状态时,调用main方法。
再看下NSBlockOperation的main方法:
open override func main() {
var blocks = [() -> Void]()
_lock()
if let existing = _block {
blocks.append(existing)
}
if let existing = _executionBlocks {
blocks.append(contentsOf: existing)
}
_unlock()
for block in blocks {
block()
}
}
NSBlockOperation的main方法中,会将block添加到数组中,然后遍历执行。
当我们自定义操作的时候,如果重写其start方法,就需要判断操作的状态,而重写main方法,就只需要处理我们自己的业务逻辑即可。通常情况下,我们只重写main方法就可以了。
二、NSOperationQueue
NSOperationQueue是操作队列,用来存放操作的。它不同于普通队列的FIFO(先进先出)的原则。对于添加的操作而言,首先会让操作进入就绪状态(就绪状态取决于操作之间的依赖关系),然后进入就绪状态的操作,它们的开始执行顺序又由操作之间相对的优先级决定。
1、 控制串行和并发
NSOperationQueue提供了两种类型的队列:主队列和并发队列
主队列如下:
//主队列
func mainQueue() {
let que = OperationQueue.main
que.addOperation {
print("1\(Thread.current)")
}
que.addOperation {
print("2\(Thread.current)")
}
que.addOperation {
print("3\(Thread.current)")
}
}
通过OperationQueue.main来创建一个主队列。在operation的block内打一个断点,通过bt查看其函数调用栈:
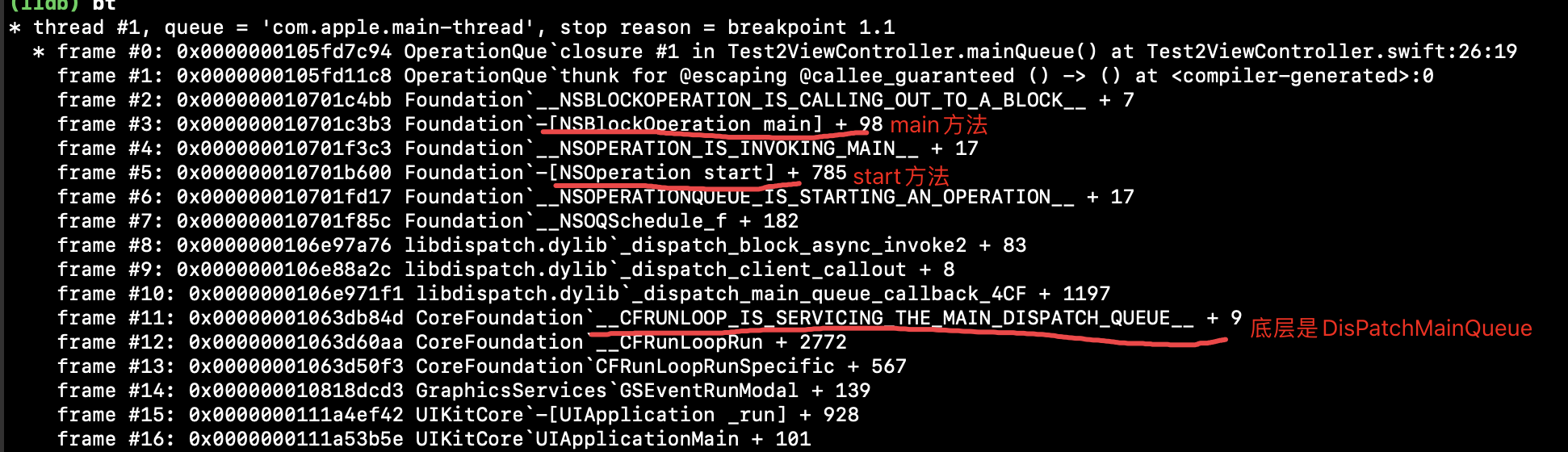
可以看到底层就是GCD的主队列。
2、并发队列可以通过设置最大并发操作数(maxConcurrentOperationCount)来控制并发和串行。
maxConcurrentOperationCount 默认情况下为-1,表示不进行限制,可进行并发执行。
extension OperationQueue {
//默认是-1
public static let defaultMaxConcurrentOperationCount: Int = -1
}
//.....
//OperationQueue 的其中一个属性:最大操作数
var __maxNumOps: Int = OperationQueue.defaultMaxConcurrentOperationCount
//.....
//对外接口
open var maxConcurrentOperationCount: Int {
get {
//返回最大操作数
return _maxNumOps
}
set(newValue) {
//当设置的最大操作数小于-1时,就会报错
if newValue < 0 && newValue != OperationQueue.defaultMaxConcurrentOperationCount {
fatalError("count (\(newValue)) cannot be negative")
}
if !__mainQ {
_lock()
//内部主要设置给_maxNumOps
_maxNumOps = newValue
//当设置为-1或者大于Int32.max时,实际的操作数__actualMaxNumOps就是最大值,所以会默认执行并发操作。
let acnt = OperationQueue.defaultMaxConcurrentOperationCount == newValue || Int32.max < newValue ? Int32.max : Int32(newValue)
//实际的操作数
__actualMaxNumOps = acnt
_unlock()
//调度
_schedule()
}
}
}
通过源码分析,可以得出以下结论:
(1)当我们设置最大并发操作数为-1或者不设置的时候,会默认并发执行。
(2)当我们设置最大并发操作数小于-1时,就会崩溃。

(3)当我们设置为0时,则不执行,当我们再次设置大于0或者-1时,会执行。
3、 maxConcurrentOperationCount 的设置流程很简单,但是maxConcurrentOperationCount是控制最大能开多少条线程吗?答案肯定不是。
maxConcurrentOperationCount是控制同一时间内,可以执行多少个不同的操作。
例如:
func concurentQueue() {
let que = OperationQueue()
que.maxConcurrentOperationCount = 1;
que.addOperation {
print("1\(Thread.current)")
sleep(1)
}
que.addOperation {
print("2\(Thread.current)")
sleep(1)
}
que.addOperation {
print("3\(Thread.current)")
}
que.addOperation {
print("4\(Thread.current)")
}
}
当maxConcurrentOperationCount=1时,打印如下:
1<NSThread: 0x60000098d2c0>{number = 6, name = (null)}
2<NSThread: 0x600000987440>{number = 7, name = (null)}
3<NSThread: 0x600000987440>{number = 7, name = (null)}
4<NSThread: 0x600000987440>{number = 7, name = (null)}
操作是按顺序执行的,也就是同一时间内,只能执行一种操作。而且开启线程数量也不是只有一条。
当maxConcurrentOperationCount=4时,打印如下:
1<NSThread: 0x6000032b3440>{number = 7, name = (null)}
4<NSThread: 0x6000032be8c0>{number = 3, name = (null)}
2<NSThread: 0x6000032bd280>{number = 6, name = (null)}
3<NSThread: 0x6000032d4400>{number = 5, name = (null)}
操作是并发执行的,也就是同一时间,可以执行4个不同的操作。
那么在底层maxConcurrentOperationCount是如何控制串行和并发的呢?带着这个问题继续探索。
三、队列的添加流程
1、NSOperationQueue的核心属性
//队列的头和尾
var __firstOperation: Unmanaged<Operation>?
var __lastOperation: Unmanaged<Operation>?
//操作数量
var __operationCount: Int = 0
//最大操作数
var __maxNumOps: Int = OperationQueue.defaultMaxConcurrentOperationCount
//实际最大操作数
var __actualMaxNumOps: Int32 = .max
//执行操作数据
var __numExecOps: Int32 = 0
2、从添加操作(_addOperation)来分析
//添加一个操作对象
open func addOperation(_ op: Operation) {
_addOperations([op], barrier: false)
}
//添加一组操作,并指定是否等待当前添加的操作组完成之后才能执行其他操作
open func addOperations(_ ops: [Operation], waitUntilFinished wait: Bool) {
_addOperations(ops, barrier: false)
if wait {
//遍历挂起操作
for op in ops {
op.waitUntilFinished()
}
}
}
//通过条件锁挂起等待
open func waitUntilFinished() {
__waitCondition.lock()
while !isFinished {
__waitCondition.wait()
}
__waitCondition.unlock()
}
//默认添加BlockOperation
open func addOperation(_ block: @escaping () -> Void) {
let op = BlockOperation(block: block)
if let qos = __propertyQoS {
op.qualityOfService = qos
}
addOperation(op)
}
//添加栅栏操作
open func addBarrierBlock(_ barrier: @escaping () -> Void) {
var queue: DispatchQueue?
_lock()
//当队列有其他操作时
if let op = __firstOperation {
let barrierOperation = _BarrierOperation(barrier)
barrierOperation.__priorityValue = Operation.QueuePriority.barrier
var iterOp: Unmanaged<Operation>? = op
//遍历链表,栅栏操作遍历添加依赖
while let operation = iterOp?.takeUnretainedValue() {
barrierOperation.addDependency(operation)
iterOp = operation.__nextOperation
}
//执行添加操作核心方法
_addOperations([barrierOperation], barrier: true)
}
//如果队列中,没有其他操作,直接通过GCD的队列来执行。
else {
queue = _synthesizeBackingQueue()
}
_unlock()
if let q = queue {
q.async(flags: .barrier, execute: barrier)
} else {
_schedule()
}
}
以上是经常用到的添加操作的方法,其中每一个方法都调用了 internal func addOperations( ops: [Operation], barrier: Bool = false)。所以继续分析:
3、_addOperations核心添加方法
//添加操作
internal func _addOperations(_ ops: [Operation], barrier: Bool = false) {
if ops.isEmpty {
return
}
//....
//遍历操作组
for op in ops {
if op._compareAndSwapState(.initialized, .enqueuing) {
successes += 1
if 0 == failures {
let retained = Unmanaged.passRetained(op)
op._cachedIsReady = op.isReady
//创建DispatchWorkItem
let schedule: DispatchWorkItem
//当操作设置了优先级,那么创建DispatchWorkItem时的flag就为.enforceQoS,默认采用DispatchWorkItem的QoS class,而不是队列的。
if let qos = op.__propertyQoS?.qosClass {
schedule = DispatchWorkItem.init(qos: qos, flags: .enforceQoS, block: {
self._schedule(op)
})
} else {
//如果操作没有设置优先级,就会根据当前gcd队列或者线程的上下文来设置。
schedule = DispatchWorkItem(flags: .assignCurrentContext, block: {
self._schedule(op)
})
}
//保存当前队列和DispatchWorkItem
op._adopt(queue: self, schedule: schedule)
op.__previousOperation = lastNewOp
op.__nextOperation = nil
if let lastNewOperation = lastNewOp?.takeUnretainedValue() {
lastNewOperation.__nextOperation = retained
} else {
firstNewOp = retained
}
lastNewOp = retained
} else {
_ = op._compareAndSwapState(.enqueuing, .initialized)
}
} else {
failures += 1
}
}
//......
if !barrier {
_lock()
//增加操作数量
_incrementOperationCount()
}
//.....
while let pendingOperation = pending?.takeUnretainedValue() {
//......
//状态改为排队成功
_ = pendingOperation._compareAndSwapState(.enqueuing, .enqueued)
var pri = pendingOperation.__priorityValue
if pri == nil {
let v = __actualMaxNumOps == 1 ? nil : pendingOperation.__propertyQoS
if let qos = v {
switch qos {
case .default: pri = Operation.QueuePriority.normal.rawValue
case .userInteractive: pri = Operation.QueuePriority.veryHigh.rawValue
case .userInitiated: pri = Operation.QueuePriority.high.rawValue
case .utility: pri = Operation.QueuePriority.low.rawValue
case .background: pri = Operation.QueuePriority.veryLow.rawValue
}
} else {
pri = Operation.QueuePriority.normal.rawValue
}
}
pendingOperation.__nextPriorityOperation = nil
if let old_last = _lastPriorityOperation(pri)?.takeUnretainedValue() {
old_last.__nextPriorityOperation = pending
} else {
//设置队列的首个优先级操作
_setFirstPriorityOperation(pri!, pending)
}
_setlastPriorityOperation(pri!, pending)
pending = pendingOperation.__nextOperation
}
//....
if !barrier {
//调度
_schedule()
}
}
在添加操作的方法中,除了对链表和栅栏操作处理外(这些细节了解就好),总结以下几点:
(1)创建DispatchWorkItem,保存任务。
(2)如果给操作设置了优先级,其实最终是设置在了DispatchWorkItem上面。
(3)最后执行_schedule()来调度。
四、DispatchWorkItem
1、DispatchWorkItem介绍
在IOS8.0之后,当我们使用swift开发时,GCD添加任务主要有两种形式,一种是常用的闭包,一种就是创建DispatchWorkItem。
DispatchWorkItem就是把任务主体,加上优先级和策略封装在一起。
比如:
let que = DispatchQueue.init(label: "xxx", qos: .userInteractive, attributes: .concurrent, autoreleaseFrequency: .inherit, target: nil)
let item = DispatchWorkItem.init(qos: .default, flags: .barrier) {
print("1\(Thread.current)")
sleep(1)
}
que.async(execute: item1)
//或者:
/*
que.async {
item1.perform()
}
*/
以上就是创建一个DispatchWorkItem,然后将它添加到GCD的并发队列,最后执行。
2、QOS
QualityOfService:服务质量,这是IOS中用来代替优先级的枚举,这里再次总结一下:
public enum QualityOfService : Int {
/* UserInteractive QoS 用于直接参与提供交互式 UI 的工作,例如处理事件或绘制到屏幕上. */
case userInteractive
/* UserInitiated QoS 用于执行用户明确请求的工作,并且必须立即呈现结果以允许进一步的用户交互。 例如,在用户在消息列表中选择电子邮件后加载它。 */
case userInitiated
/* 实用程序 QoS 用于执行用户不太可能立即等待结果的工作。 这项工作可能已由用户请求或自动启动,不会阻止用户进行进一步的交互,通常在用户可见的时间尺度上运行,并且可能通过非模态进度指示器向用户指示其进度。 这项工作将以节能的方式运行,以在资源受限时遵循更高的 QoS 工作。 例如,定期内容更新或媒体导入等批量文件操作。 */
case utility
/* 后台 QoS 用于非用户发起或不可见的工作。 通常,用户甚至不知道这项工作正在发生,它将以最有效的方式运行,同时对更高 QoS 的工作给予最大的尊重。 例如,预取内容、搜索索引、备份以及与外部系统同步数据。 */
case background
/* 默认 QoS 表示没有 QoS 信息。 尽可能从其他来源推断出 QoS 信息。 如果无法进行此类推断,则将使用 UserInitiated 和 Utility 之间的 QoS。 */
case `default`
}
3、DispatchWorkItem的flag
1、enforceQoS 表明DispatchWorkItem会采用当前的QoS class,而不是队列的。
2、inheritQoS 表明DispatchWorkItem会采用队列的QoS class,而不是当前的。
3、noQoS 不指定QoS,由调用线程或队列来指定。
4、barrier 如果DispatchWorkItem被提交到.concurrent并发队列,那么这个DispatchWorkItem中的操作会具有独占性(防止此DispatchWorkItem中的block内的操作与其他操作同时执行)。
如果直接执行这个DispatchWorkItem,没有任何效果(因为没有其他的item了)。(相当于异步栏栅)
5、detached 这个选项是系统不会把当前线程或者队列的属性设置应用在这个任务上。
6、assignCurrentContext 这个选项会使任务使用所在队列或者线程(或者说当前执行上下文)的属性设置,比如优先级。
五、队列的执行流程
通过对添加操作流程的分析和DispatchWorkItem的总结,继续来分析队列执行的核心流程。
//核心调度
internal func _schedule() {
var retestOps = [Operation]()
_lock()
//可用操作数量 = 实际最大操作数 - 执行操作数
//假如最大操作数 = 1时,执行操作数默认为0,所以这里可用操作数量就为1。
var slotsAvail = __actualMaxNumOps - __numExecOps
for prio in Operation.QueuePriority.priorities {
//当slotsAvail <= 0时,也就不执行,此时需要等待其他操作完成,这也就是设置最大操作数的原理。
if 0 >= slotsAvail || _suspended {
//可用数量为0 或者 被挂起,不执行
break
}
//根据优先级获取队列 (可能为nil)
var op = _firstPriorityOperation(prio)
var prev: Unmanaged<Operation>?
//遍历链表
while let operation = op?.takeUnretainedValue() {
if 0 >= slotsAvail || _suspended {
//可用数量为0 或者 被挂起,不执行
break
}
let next = operation.__nextPriorityOperation
var retest = false
// if the cached state is possibly not valid then the isReady value needs to be re-updated
//operation._fetchCachedIsReady(&retest) 判断是否有依赖
if Operation.__NSOperationState.enqueued == operation._state && operation._fetchCachedIsReady(&retest) {
if let previous = prev?.takeUnretainedValue() {
previous.__nextPriorityOperation = next
} else {
//设置队列的首个优先级操作
_setFirstPriorityOperation(prio, next)
}
if next == nil {
_setlastPriorityOperation(prio, prev)
}
operation.__nextPriorityOperation = nil
operation._state = .dispatching
//执行操作数量++
_incrementExecutingOperations()
//可用操作数量--
slotsAvail -= 1
let queue: DispatchQueue
if __mainQ {
queue = DispatchQueue.main
} else {
queue = __dispatch_queue ?? _synthesizeBackingQueue()
}
//执行schedule
if let schedule = operation.__schedule {
if operation is _BarrierOperation {
queue.async(flags: .barrier, execute: {
schedule.perform()
})
} else {
queue.async(execute: schedule)
}
}
op = next
} else {
if retest {
retestOps.append(operation)
}
prev = op
op = next
}
}
}
_unlock()
for op in retestOps {
if op.isReady {
op._cachedIsReady = true
}
}
}
通过核心流程的源码分析,可以总结一下:
(1)回到上面提到的问题“maxConcurrentOperationCount是如何控制串行和并发的呢?”,答案已经很清晰了,通过可用操作的数据来控制串行和并发操作的。(可用操作数量 = 实际最大操作数 - 执行操作数)
当可用操作数大于1时,如果再添加操作,可以继续执行。当可用操作数为0,如果再添加操作,就需要等当前操作执行完之后再执行,保证了串行。
(2)当操作满足一下3个条件时,会去调度执行workitem。
<1>可用操作数>0
<2>是否为就绪状态 (取决于是否有依赖)
open var isReady: Bool {
_lock()
defer { _unlock() }
return __unfinishedDependencyCount == 0
}
internal func _fetchCachedIsReady(_ retest: inout Bool) -> Bool {
let setting = _cachedIsReady
if !setting {
_lock()
//当没有依赖的时候
retest = __unfinishedDependencyCount == 0
_unlock()
}
return setting
}
<3>操作状态为enqueued
(3)异步执行workItem之后,就会来到OperationQueue的 func schedule( op: Operation)方法。
internal func _schedule(_ op: Operation) {
op._state = .starting
// set current tsd
OperationQueue._currentQueue.set(self)
op.start()
OperationQueue._currentQueue.clear()
// We've just cleared _currentQueue storage.
// NSThreadSpecific doesn't release stored value on clear.
// This means `self` will leak if we don't release manually.
Unmanaged.passUnretained(self).release()
// unset current tsd
if op.isFinished && op._state.rawValue < Operation.__NSOperationState.finishing.rawValue {
Operation.observeValue(forKeyPath: _NSOperationIsFinished, ofObject: op)
}
}
这个方法会执行操作的start方法。之后会主动发出完成状态通知
if op.isFinished && op._state.rawValue < Operation.__NSOperationState.finishing.rawValue {
Operation.observeValue(forKeyPath: _NSOperationIsFinished, ofObject: op)
}
六、NSOperation添加依赖
直接来看添加依赖的核心方法:
internal func _addDependency(_ op: Operation) {
withExtendedLifetime(self) {
withExtendedLifetime(op) {
var up: Operation?
_lock()
if __dependencies.first(where: { $0 === op }) == nil {
__dependencies.append(op)
up = op
}
_unlock()
if let upwards = up {
upwards._lock()
_lock()
let upIsFinished = upwards._state == __NSOperationState.finished
if !upIsFinished && !_isCancelled {
assert(_unfinishedDependencyCount >= 0)
//增加依赖计数
_incrementUnfinishedDependencyCount()
//增加依赖
upwards._addParent(self)
}
_unlock()
upwards._unlock()
}
Operation.observeValue(forKeyPath: _NSOperationIsReady, ofObject: self)
}
}
}
(1)首先将依赖的操作添加到__dependencies数组中。
(2)增加依赖计数。
(3)反向添加依赖到__downDependencies。(也就是被依赖的操作集合)
internal func _addParent(_ parent: Operation) {
__downDependencies.insert(PointerHashedUnmanagedBox(contents: .passUnretained(parent)))
}
再来看被依赖的操作执行完,依赖的操作是如何执行的。
核心监听方法:
internal static func observeValue(forKeyPath keyPath: String, ofObject op: Operation) {
//内部状态
enum Transition {
case toFinished
case toExecuting
case toReady
}
//状态转换
let kind: Transition?
if keyPath == _NSOperationIsFinished || keyPath == _NSOperationIsFinishedAlternate {
kind = .toFinished
} else if keyPath == _NSOperationIsExecuting || keyPath == _NSOperationIsExecutingAlternate {
kind = .toExecuting
} else if keyPath == _NSOperationIsReady || keyPath == _NSOperationIsReadyAlternate {
kind = .toReady
} else {
kind = nil
}
if let transition = kind {
switch transition {
case .toFinished: // we only care about NO -> YES
if !op.isFinished {
return
}
var ready_deps = [Operation]()
op._lock()
let state = op._state
if op.__queue != nil && state.rawValue < __NSOperationState.starting.rawValue {
print("*** \(type(of: op)) \(Unmanaged.passUnretained(op).toOpaque()) went isFinished=YES without being started by the queue it is in")
}
if state.rawValue < __NSOperationState.finishing.rawValue {
op._state = .finishing
} else if state == .finished {
op._unlock()
return
}
//取依赖当前"完成操作"的操作(比如a依赖b,那么就是取a)
let down_deps = op.__downDependencies
op.__downDependencies.removeAll()
if 0 < down_deps.count {
for down in down_deps {
let idown = down.contents.takeUnretainedValue()
idown._lock()
if idown._unfinishedDependencyCount == 1 {
//未完成依赖的数量为1时
ready_deps.append(idown)
} else if idown._unfinishedDependencyCount > 1 {
//未完成依赖的数量为大于1时,不用加入到ready_deps,因为它还依赖了其他操作
idown._decrementUnfinishedDependencyCount()
} else {
assert(idown._unfinishedDependencyCount == 0)
assert(idown._isCancelled == true)
}
idown._unlock()
}
}
op._state = .finished
//当前操作中保存的que
let oq = op.__queue
op.__queue = nil
op._unlock()
if 0 < ready_deps.count {
for down in ready_deps {
down._lock()
if down._unfinishedDependencyCount >= 1 {
down._decrementUnfinishedDependencyCount()
}
down._unlock()
//就绪状态
Operation.observeValue(forKeyPath: _NSOperationIsReady, ofObject: down)
}
}
op.__waitCondition.lock()
//通知挂起的操作继续执行
op.__waitCondition.broadcast()
op.__waitCondition.unlock()
if let complete = op.__completion {
let held = Unmanaged.passRetained(op)
DispatchQueue.global(qos: .default).async {
complete()
held.release()
}
}
//完成的时候通知op完成操作
if let queue = oq {
queue.takeUnretainedValue()._operationFinished(op, state)
//这里release的是当前操作中保存的que
queue.release()
}
case .toExecuting:
let isExecuting = op.isExecuting
op._lock()
if op._state.rawValue < __NSOperationState.executing.rawValue && isExecuting {
op._state = .executing
}
op._unlock()
case .toReady:
let r = op.isReady
op._cachedIsReady = r
//op如果被添加到对应的queue中则触发
let q = op._queue
if r {
//调度3
q?._schedule()
}
}
}
}
可以看到当完成状态时,会从__downDependencies取出idown操作,然后将其状态改为就绪状态。 进入就绪状态之后,又会走_schedule()方法。
七、NSOperation添加额外操作
NSOperation的额外操作和整个队列的执行流程关系就不大了,额外操作是在main方法中执行的。
先来看添加:
open func addExecutionBlock(_ block: @escaping () -> Void) {
if isExecuting || isFinished {
fatalError("blocks cannot be added after the operation has started executing or finished")
}
_lock()
defer { _unlock() }
if _block == nil {
_block = block
} else if _executionBlocks == nil {
_executionBlocks = [block]
} else {
_executionBlocks?.append(block)
}
}
底层会有一个_executionBlocks数组,存放所有额外操作的block。
open override func main() {
var blocks = [() -> Void]()
_lock()
if let existing = _block {
blocks.append(existing)
}
if let existing = _executionBlocks {
blocks.append(contentsOf: existing)
}
_unlock()
for block in blocks {
block()
}
}
当执行时,也是在main方法中去遍历执行的。
在main方法中,可以看到:
for block in blocks {
block()
}
是没有加锁的,所以额外操作有可能在不同的线程去执行(系统决定)。