OC底层 - 内存平移&Method Swizzling
前言
一、内存平移
二、Method Swizzling 浅谈
今天主要记录两个比较重要的知识点,一个是内存平移,一个是Method Swizzling。
一、内存平移
新建一个MyTestClass:
@interface MyTestClass : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *testStr;
- (void)doTest;
@end
@implementation MyTestClass
- (void)doTest {
NSLog(@"123");
NSLog(@"%@",self.testStr);
}
@end
在ViewController中初始化:
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "MyTestClass.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
Class cls = [MyTestClass class];
void *test = &cls;
[(__bridge id)test doTest];
MyTestClass *testClass = [MyTestClass alloc];
[testClass doTest];
}
@end
以上代码,提出两个问题:
(1)通过 [(__bridge id)test doTest] 可以调用吗?和[testClass doTest] 调用有区别吗?
(2)在doTest方法中,self.testStr分别打印的是什么?
1、[(__bridge id)test doTest] 和 [testClass doTest]; 调用是一样的。
先看[testClass doTest] 因为testClass对象的第一个成员变量就是isa,也就是testClass的首地址指向isa,而isa中就包含有类信息。
对于 [(__bridge id)test doTest] 来说,test是cls的指针,同样指向了MyTestClass。
它们通过objc_msgSend去查找方法的时候,都是去查找MyTestClass类中的methodList中的doTest方法。所以它们的调用是一样的。
2、在[(__bridge id)test doTest] 中self.testStr打印为<ViewController: 0x7xxxxxxx> 而在 [testClass doTest] 中 打印为nil。
先看 [testClass doTest] ,我们知道testClass中第一个成员是isa,第二个成员是testStr,要想找到testStr,只需要将首地址平移8字节。
同理[(__bridge id)test doTest] 也会因为模仿去找testStr而将地址平移8个字节。就会指向ViewController。
3、压栈
test 平移8个字节,为什么会指向ViewController呢?
从viewDidLoad方法开始,里面的所有变量都是有栈桢指向的。由于栈是8字节对齐,并且由高地址指向低地址。所以如下图: (压栈的顺序)
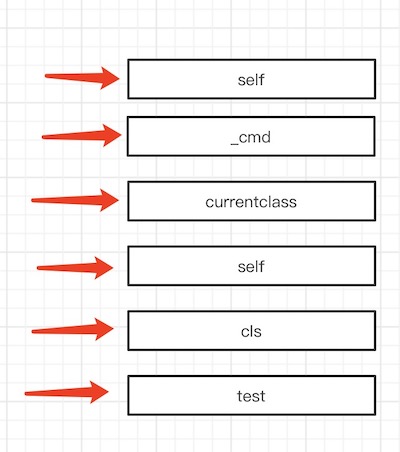
图中的self 和 currentclass 是指,[super viewDidLoad] 中的super结构体:
struct objc_super2 {
id receiver;
Class current_class;
};
_cmd和self是指viewDidLoad的两个隐藏参数,隐藏参数同样会压入栈桢。
回到doTest方法中:
- (void)doTest {
NSLog(@"%@",self.testStr);
}
self.testStr中的self,是消息接收者(栈地址)。
这个栈地址指向图中的cls,它平移8字节之后,就指向了图中的self,图中的self就是当前的ViewController。
所以在[(__bridge id)test doTest] 中self.testStr打印为<ViewController: 0x7xxxxxx>。
4、当前栈的具体情况
先确定几个压栈的规则:
(1)参数会从前往后一直压入
(2)结构体的属性是从后往前一直压入
例如:
struct testStruct {
id test1;
id test2;
};
打印:
(lldb) p &stu.test1
(id *) $3 = 0x00007ffee85da050
(lldb) p &stu.test2
(id *) $4 = 0x00007ffee85da058
(lldb)
5、通过代码打印栈的情况
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
Class cls = [MyTestClass class];
void *test = &cls;
[(__bridge id)test doTest];
int a = 5;
int *b = &a;
int **c = &b;
NSLog(@"%p,%i",b,*b);
NSLog(@"%i",**c);
//测试代码
//oc
NSObject *obj = [NSObject alloc];
NSObject * __strong*objRef = &obj;
NSLog(@"%p,%@",objRef,(NSObject *)(*objRef));
//c
void *objRef2 = &obj;
NSLog(@"%p,%@",objRef2, *(void **)objRef2);
//隐藏参数,会压入栈桢(self为第一个隐藏参数,而隐藏参数又是从前往后压栈,所以)
void *sp = (void *)&self;
void *end = (void *)&test;
long count = (sp - end) / 0x8;
for (int i =0; i < count; i ++) {
void *address = sp - i * 0x8;
if (i == 1) {
NSLog(@"%p = %s \n",address, *(char **)address);
} else {
NSLog(@"%p = %@ \n",address, *(void **)address);
}
}
}
6、继续增加难度
@interface MyTestClass : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *test_name;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *testStr;
- (void)doTest;
@end
我们如果在testStr上面在增加一个属性test_name。那么doTest会输出什么呢?
答案很简单,会是ViewController,因为继续平移8字节嘛。
那么如果添加的是 “@property (nonatomic, assign) int test_name;”呢?
答案依然是ViewController, 还记得内存对齐原则吗(可以看下oc对象原理),虽然test_name是int类型,4字节。但是系统把testStr从test_name位置开始,向后继续平移4个字节,到8个字节的位置开始排放(保证能被8整除)。
继续修改成:
@interface MyTestClass : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *test_name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int testStr;
- (void)doTest;
@end
这时,在读取testStr的时候会直接崩溃。
直接clang 编译下输出c++
struct MyTestClass_IMPL {
struct NSObject_IMPL NSObject_IVARS; //8
int _testStr; //4
NSString * _Nonnull _test_name; //8
};
编译器会默认把int类型提前放置,然后当我们在读取testStr的是,此时是平移了4个字节。但是平移4个字节之后是指向到<ViewController: 0x7xxxxxx>的一半,所以直接报错了,非法地址(EXC_BAD_ACCESS )。
二、Method Swizzling 浅谈
Method Swizzling 不仅在面试中经常会被问到,而且在日常的开发过程中,也经常会被用来面向切面编程。以及在逆向领域也是一把利器。
对于普通的开发人员来说,可能这个“黑魔法”就是一个简单的方法交换,网上随便粘几句代码就能实现基本的功能。但在我之前经历的一些项目中,会发现有很多滥用的情况。所以针对Method Swizzling的相关问题,很有必要做下总结(日后会结合c/c++等的hook原理再做具体分析)。
1、一个简单的例子
+ (void)methodSwizzlingWithClass:(Class)cls oriSEL:(SEL)oriSEL swizzledSEL:(SEL)swizzledSEL {
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, oriSEL);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL);
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
//底层
/*
void method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2) {
if (!m1 || !m2) return;
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
//获取imp
IMP imp1 = m1->imp(false);
IMP imp2 = m2->imp(false);
//获取sel
SEL sel1 = m1->name();
SEL sel2 = m2->name();
//交换 imp
m1->setImp(imp2);
m2->setImp(imp1);
//刷新缓存
flushCaches(nil, __func__, [sel1, sel2, imp1, imp2](Class c){
return c->cache.shouldFlush(sel1, imp1) || c->cache.shouldFlush(sel2, imp2);
});
adjustCustomFlagsForMethodChange(nil, m1);
adjustCustomFlagsForMethodChange(nil, m2);
}
*/
以上代码,可以简单的写出方法交换。通过底层代码也可以看出,方法交换,交换的是imp。
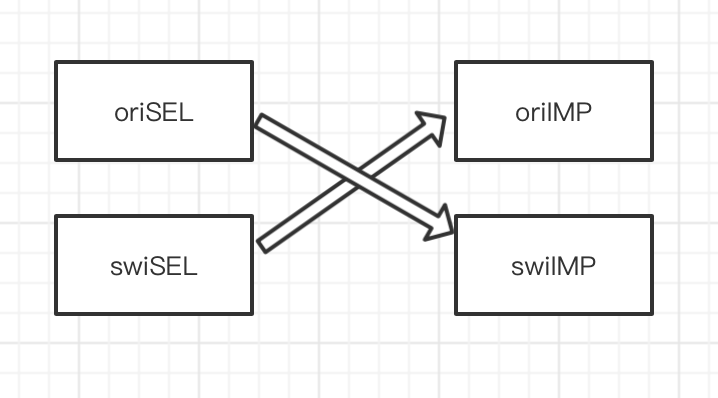
那么此时我就可以直接在一个类的分类里面这样写:
#import "MyTestSubObject+Test.h"
#import "MyMethodSwizzlingTools.h"
@implementation MyTestSubObject (Test)
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodSwizzlingWithClass:self oriSEL:@selector(test1) swizzledSEL:@selector(test1_hook)];
});
}
- (void)test1_hook {
//这里不会递归,因为新的sel指向了,原来的imp
[self test1_hook];
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
@end
重点:
(1)为了保证一次性的问题,所以加上了dispatch_once;
(2)如果不加dispatch_once的话,那么有可能会走多次。再走一次,方法又重新交换回来了,就没有意义了。
(3)load方法会将类变成非懒加载类,造成启动速度下降,所以可以考虑在+ (void)initialize方法中去做方法交换。
2、第一个坑点 - (子类没有实现,父类实现)
#import "MyTestSuperObject.h"
@implementation MyTestSuperObject
- (void)testSutper {
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
@end
我只在父类实现- (void)testSutper,子类不实现。然后在子类去做方法交换。
.....
@implementation MyTestSubObject (Test)
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
//hook当前类的实例方法
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodSwizzlingWithClass:self oriSEL:@selector(test1) swizzledSEL:@selector(test1_hook)];
//hook 只有父类实现的方法
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodSwizzlingWithClass:self oriSEL:@selector(testSutper) swizzledSEL:@selector(testSutper_hook)];
});
}
- (void)testSutper_hook {
[self testSutper_hook];
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
.....
在外层调用:
MyTestSubObject *sub = [MyTestSubObject alloc];
[sub testSutper];
MyTestSuperObject *superObj = [MyTestSuperObject alloc];
[superObj testSutper];
此时一运行,就会报错:'-[MyTestSuperObject testSutper_hook]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x6000037d41b0'
父类找不到testSutper_hook方法。
原因是:
(1) 当子类把父类的方法交换之后,父类中“testSutper”方法的sel指向了子类中的imp,子类交换的方法“testSutper_hook”的sel,指向了原来父类方法的imp。
(2) 当子类去调用“testSutper”方法的时候,会来到“testSutper_hook”imp。在testSutper_hook方法中又调用“ [self testSutper_hook];”,也就调用了原来的imp实现。没有任何问题。
(3) 当父类去调用“testSutper”方法的时候,同样会来到“testSutper_hook”imp。但是在调用“ [self testSutper_hook];”的时候,父类会进行方法查找流程,方法查找是通过sel去查找的,因为父类中本身就不存在testSutper_hook这个sel。所以会报错。
优化刚刚的方法交换的实现:
+ (void)methodBetterSwizzlingWithClass:(Class)cls oriSEL:(SEL)oriSEL swizzledSEL:(SEL)swizzledSEL {
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, oriSEL);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL);
//方法一:
BOOL success = class_addMethod(cls, oriSEL, method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod));
if (success) {
//添加成功,直接替换
class_replaceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL, method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
} else {
//存在
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
//方法二(很少用,1是oriMethod有可能是nil,2是就算添加成功之后,还要再获取一遍方法。):
// BOOL success = class_addMethod(cls, oriSEL, method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
// if (success) {
// //此时oriMethod应该再获取一遍,获取到本类的方法,而不是父类的。
// oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, oriSEL);
// method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swizzledMethod);
// } else {
// method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swizzledMethod);
// }
}
这里有2个方法可以解决,但是其根本原理都是一样的,主要用方法一:
尝试添加oriSEL,并且对应的imp是要交换方法的imp。(1)如果添加成功,证明本类没有oriSEL。此时注意,oriSEL指向了要交换方法的imp,而swizzledSEL也指向了要交换方法的imp。所以只需要把swizzledSEL指向的imp替换为原来方法的imp即可。(2)如果添加失败,证明原来本类存在oriSEL,那么直接做方法交换即可。
3、交换构造方法
//hook当前类的构造方法
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodBetterSwizzlingWithClass:self
oriSEL:@selector(init) swizzledSEL:@selector(init_hook)];
//hook当前类的alloc
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodBetterSwizzlingWithClass:
objc_getMetaClass("MyTestSubObject")
oriSEL:@selector(alloc) swizzledSEL:@selector(alloc_hook)];
这里我们分别交换init和alloc方法。
主要注意2点:
(1)因为本类很可能没有实现alloc和init方法,而是使用的父类(NSObject)的alloc和init方法。所以我们需要在交换之前,先去尝试添加alloc和init方法。
(2)alloc方法是类方法,存在元类中,所以我们传入的是objc_getMetaClass("MyTestSubObject") 。
4、第二个坑点 - (子类和父类都没有实现)
//hook子类和父类都没有的方法
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodBetterSwizzlingWithClass:self
oriSEL:@selector(noMethod) swizzledSEL:@selector(noMethod_hook)];
- (void)noMethod_hook {
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
[self noMethod_hook];
}
如上代码,我交换了一个子类和父类都没有实现的方法“noMethod”,此时会有什么现象呢。
运行之后,发现是无限递归调用了。
原因是因为,在进行“class_replaceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL, method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));”的时候,替换了一个空的imp,没有替换成功。所以“noMethod_hook”仍然指向要交换的imp,就会一直递归调用。
所以我们需要继续优化交换代码:
+ (void)methodBestSwizzlingWithClass:(Class)cls oriSEL:(SEL)oriSEL swizzledSEL:(SEL)swizzledSEL {
if (!cls) NSLog(@"传入的交换类不能为空");
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, oriSEL);
Method swiMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL);
if (!swiMethod) {
NSLog(@"传入的交换方法不能为空");
}
if (!oriMethod) { // 避免动作没有意义
// 在oriMethod为nil时,替换后将swizzledSEL复制一个不做任何事的空实现,代码如下:
class_addMethod(cls, oriSEL, method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
//核心代码
method_setImplementation(swiMethod, imp_implementationWithBlock(^(id self, SEL _cmd){
NSLog(@"来了一个空的 ori imp");
}));
}
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(cls, oriSEL, method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL, method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
} else {
//oriMethod可能为nil,如果为nil,交换失败
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swiMethod);
}
}
因为当oriMethod为nil时,swizzledSEL会替换imp失败,所以在给oriSEL添加好方法之后,再设置一个imp给swizzledSEL。就解决问题了。
5、交换其他类的方法
#import "MyTextOtherObject.h"
@implementation MyTextOtherObject
- (void)test {
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
@end
我在MyTestSubObject中,去交换MyTextOtherObject中的test方法。
@implementation MyTestSubObject (Test)
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
//hook当前类的实例方法
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodSwizzlingWithClass:self oriSEL:@selector(test1) swizzledSEL:@selector(test1_hook)];
//hook 只有父类实现的方法
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodSwizzlingWithClass:self oriSEL:@selector(testSutper) swizzledSEL:@selector(testSutper_hook)];
//hook当前类的构造方法
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodBetterSwizzlingWithClass:self oriSEL:@selector(init) swizzledSEL:@selector(init_hook)];
//hook当前类的alloc
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodBetterSwizzlingWithClass:objc_getMetaClass("MyTestSubObject") oriSEL:@selector(alloc) swizzledSEL:@selector(alloc_hook)];
//hook子类和父类都没有的方法
[MyMethodSwizzlingTools methodBestSwizzlingWithClass:self oriSEL:@selector(noMethod) swizzledSEL:@selector(noMethod_hook)];
//hook其他类的方法
//(1)获取要交换方法的那个类
Class oriClass = objc_getClass("MyTextOtherObject");
//(2)要交换的方法
SEL oriSEL = @selector(test);
//(3)获取要交换的那个方法的imp,并记录
oriImp = method_getImplementation(class_getInstanceMethod(oriClass, oriSEL));
class_replaceMethod(oriClass, oriSEL, (IMP)test_other_hook, method_getTypeEncoding(class_getInstanceMethod(oriClass, oriSEL)));
});
}
IMP (*oriImp)(id self,SEL _cmd);
void test_other_hook(id self,SEL _cmd) {
oriImp(self,_cmd);
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
- (void)test1_hook {
//这里不会递归,因为新的sel指向了,原来的imp
[self test1_hook];
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
- (void)testSutper_hook {
[self testSutper_hook];
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
- (id)init_hook {
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
return [self init_hook];
}
//alloc -> objc_alloc -> calloc -> objc_msgSend -> alloc -> _objc_rootAlloc -> calloc -> objc_rootAllctWithZone -> class_createInstanceFromZone
+ (void)alloc_hook {
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
[self alloc_hook];
}
- (void)test_hook {
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
}
- (void)noMethod_hook {
NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__);
[self noMethod_hook];
}
@end
如何要hook其他类的方法,核心的原理就是记录原始的imp。hook其他类的方法主要用于逆向领域,我们就先不展开讨论了。今后会结合fishhook具体的分析更多的场景。